Difference between the areas beyond each Z score. A data analyst performs a correlation analysis between two quantities.
The ANOVA method assesses the relative size of variance among group means between group variance compared to the average variance.
. One quantity - distance - accumulates the amount of total change of location over the course of a motion. Distribution refers to the frequencies of different responses. X1 is the mean value for sample 1.
There are two quantities that are used to describe the changing location. When we compare a sample with a theoretical distribution we can use a Monte Carlo simulation to create a test statistics distribution. A True B False Answer.
If the observed data perfectly follow a normal distribution the value of the KS statistic will be 0. In this course we will be using Pearsons r as a measure of the linear relationship between two quantitative variables. The first formula becomes.
There is a sample from each of these populations and thus there are degrees of freedom for both of these samples. By the two-point formula the equation of a line through points is. The sample data follow the hypothesized distribution.
To find proportion of the area under the normal curve between two Z scores that are both above the mean it is necessary to examine the. The test relies on a set of assumptions for it to. The P-Value is used to decide whether the difference is large enough to reject the null hypothesis.
It is because that the relative location of the several group means can be more conveniently identified by variance among the group means than comparing many group means directly when number of means are large. If the data is normally distributed the two-sample t-test for two independent groups and the paired t-test for matched samples are probably the most widely used methods in statistics for the comparison of differences between two samples. Answer the question True or False.
The 3 main types of descriptive statistics concern the frequency distribution central tendency and variability of a dataset. N1 is the number of people from the 1st sample who provided a response to the survey. It can be used only when x and y are from normal distribution.
Where R1 refers to the sum of the ranks for the first group and R2 refers to the sum of the ranks for the second group. Like any statistical hypothesis test distribution tests have a null hypothesis and an alternative hypothesis. Statistics from these populations combine in a fraction.
T is the t-statistic. X2 is the mean value for sample 2. Since solve for.
Which term is used to describe the right and left ends of a distribution graph. An independent samples t-test is used when you want to compare the means of a normally distributed interval dependent variable for two independent groups. The second one is 1020 or 05.
If the two quantities are proportional their ratio should never change. By repeating this process 1000. Where the slope of the line.
Product obtained by multiplying the smaller Z score by the larger Z score. The two variables have no relationship. Pearsons r can easily.
Although this fact is well documented in statistical literature confusion exists with regard to the use of these two test. What does this mean. Pearson correlation r which measures a linear dependence between two variables x and y.
N2 is the number of people from the 2nd sample who provided a response to the survey. The third one is 1537 or about 041. In a sample we use the symbol r.
Up to 10 cash back Correct answer. Mode the most frequent score score that shows up more than. In fact we subtract one from both of the sample sizes to determine our two numbers of degrees of freedom.
The choice of the two points from the given four is arbitrary so we will select the middle two ordered pairs. Quotient obtained by dividing the larger Z score by the smaller. The Test Statistic of the KS Test is the Kolmogorov Smirnov Statistic which follows a Kolmogorov distribution if the null hypothesis is true.
Which term is used to describe a graph of distribution where the peak is left of. For instance if we want to test whether a p-value distribution is uniformly distributed ie. Distance is the amount of ground that is covered.
It may be any set. For example using the hsb2 data file say we wish to test whether the mean for write is the same for males and females. Measures of variability show you the spread or dispersion of your dataset.
P-value uniformity test or not we can simulate uniform random variables and compute the KS test statistic. F b2S x 21 S ε 2N-2 Select a X confidence level H0. A set of real numbers a set of vectors a set of arbitrary non-numerical values etcFor example the sample space of a coin flip would be.
Mean the average score the sum of the scores divided by the total number of scores ΣX N Point 2. The result of the analysis is an r value of 0. N1 and n2 refer to the sample populations of the the first and second group.
A probability distribution is a mathematical description of the probabilities of events subsets of the sample spaceThe sample space often denoted by is the set of all possible outcomes of a random phenomenon being observed. β 0 ie variation in y is not explained by the linear regression but rather by chance or fluctuations H1. Median the middle score score that divides distribution in half.
Its also known as a parametric correlation test because it depends to the distribution of the data. Your first ratio is 59 or about 055. 249 The exponential distribution is sometimes called the waiting-time distribution because it is used to describe the length of time between occurrences of random events.
The plot of y f x is named the linear regression curve. A t-test is a statistic method used to determine if there is a significant difference between the means of two groups based on a sample of data. The test statistic associated with the Mann-Whitney U Test is defined as U where U is the smaller of the two values U1 and U2 defined via the following set of equations.
Sx1x2 is the standard deviation. The F-distribution is derived from a ratio involving two populations. We then use F-statistics to test the ratio of the variance explained by the regression and the variance not explained by the regression.
The second quantity - displacement - only. Measures of central tendency give you the average for each response. T-test groups female 0 1 variables write.
Distribution tests are hypothesis tests that determine whether your sample data were drawn from a population that follows a hypothesized probability distribution. In a population we use the Greek letter ρ rho.
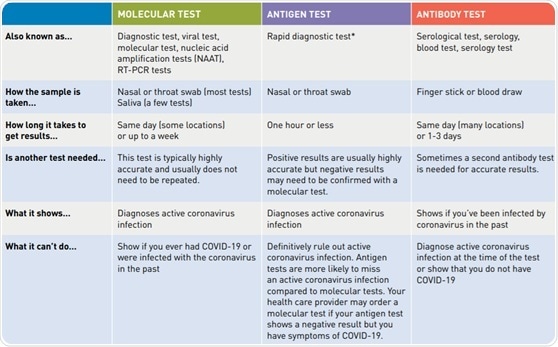
Sensitive And Accurate Diagnostic Tests Of Covid 19 With High Quality Sars Cov 2 Proteins

0 Comments